Coexistence and Migration of 4G to 5G
Explore seamless 4G to 5G migration with ABot, supporting NSA/SA options, dual connectivity, and Vo5G validation for operators.
Spectrum allocation for 5G is going on world-wide. So MNOs and ISPs are gearing up to upgrade their LTE network to 5G. ETSI 3GPP has defined 5G Access Network as NR or New Radio and the 5G Packet Core as 5GC. The 5G base station is called gNB (or Next Generation NodeB). It has set some guidelines in the form of Non Standalone (NSA) and Standalone (SA) ways of implementing 5G network infrastructure. Depending on the availability of OEM implementation, the operators can choose a path of upgrading to 5G.
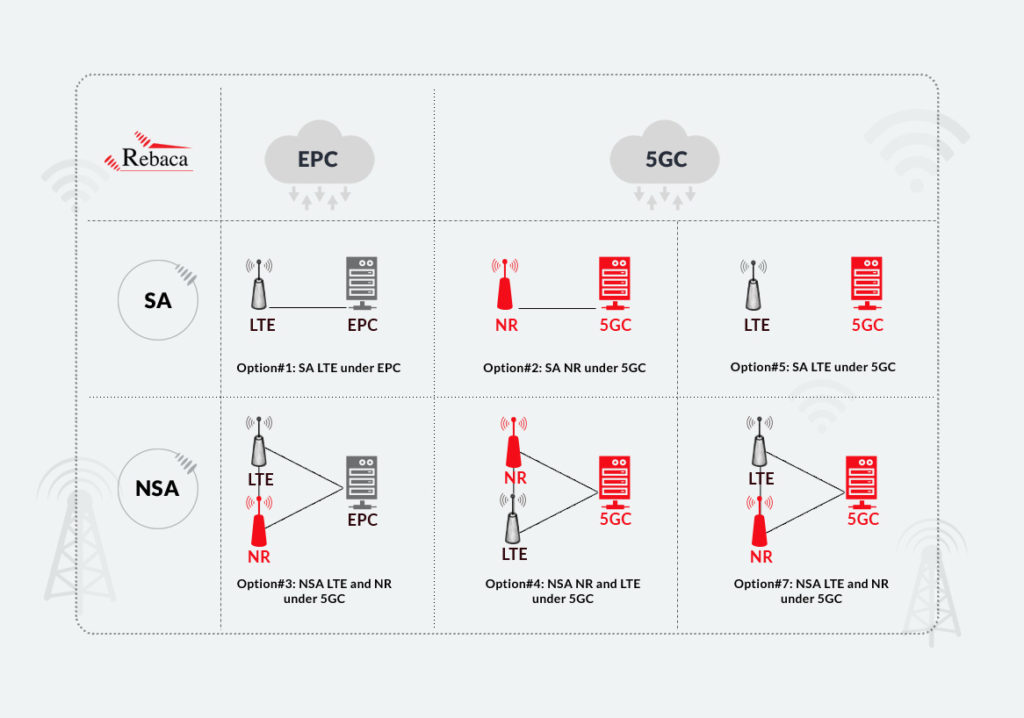
NSA means co-existence of LTE and 5G infrastructure and requires upgrade of the Access Network, with the 4G Packet Core supporting dual connectivity with both 4G eNB and 5G gNB. Dual Connectivity means one is the master base station and the other is the secondary base station. Although using the EPC as the packet core will limit the usage of NR, still operators choose NSA mode for upgrading to 5G. Because augmenting the existing infrastructure accelerates the availability of 5G services and reduces the initial investment.
There are 3 options laid forward for NSA – Option 3, Option 4 and Option 7, and some variants for each option. Option 3 has three variants – 3, 3a and 3x.
- Option-3 — Data to and from the network flows through evolved Node Base and EPC, and some part of the data can be transferred to gNB over X2 interface between eNB and gNB. But gNB does not communicate with EPC.
- Option-3a — Data traffic is split at the EPC (SGW) and both evolved Node Base and gNB communicate with the EPC over S1-U, and there is no X2 communication between eNB and gNB. So scenarios it can support voice traffic through eNB and data traffic through gNB.
- Option-3x — Data traffic is split across 4G and 5G at 5G gNB. Data flows to and from the network through gNB and EPC over S1-U and control plane is carried over S1-MME from eNB to EPC, a part of the data is split between gNB and eNB over the X2 interface.
In NSA option 4, 5GC replaces EPC, eNB is upgraded to Next Generation eNB (NG eNB) and both NG eNB and gNB should connect to 5GC, but NG eNB has only the NG-U interface to 5GC. gNB has both the NG-U and NG-C interfaces. NG eNB and gNB connects over the Xn interface. This option is capable of serving some new 5G applications. The interface between gNB and AMF is also called N2 and the interface between gNB and UPF is called N3, so the control plane is over N2 and user plane is over N3. Option 4 has two variants – 4 and 4a.
- Option-4 – NG eNB is not connected to 5GC hence data traffic is split over the Xn interface. gNB is connected to 5GC with NG-U and NG-C.
- Option-4a – NG evolved Node Base is not connected to gNB over Xn, but it is connected to 5GC over the NG-U interface. gNB has both NG-U and NG-C interface. Data traffic is split between 4G and 5G at 5GC (UPF).
In NSA option 7, 5GC replaces the EPC, eNB and gNB both should connect to 5GC, hence the eNB needs to be upgraded to NGeNB with capabilities of connecting the 5GC over NGAP protocol. NG eNB has NG-U and NG-C interfaces to 5GC and NG eNB connects with gNB over Xn. Serving new 5G applications would be possible using NSA option 7. Option 7 has three variants – 7, 7a, 7x.
- Option-7 – gNB does not communicate to 5GC. Data traffic flows through NG eNB communicating to and from 5GC. Some part of the data can be transferred through gNB over the Xn interface.
- Option-7a – NG eNB and gNB are not connected via Xn and instead gNB is connected to 5GC over NG-U. NG eNB is connected to 5GC over NG-C and NG-U. Data traffic is split at the 5GC (UPF).
- Option-7x – Data traffic is split across NG evolved Node Base and gNB by gNB. Data flows to and from the network through gNB and 5GC over NG-U and control plane is carried over NG-C from NG eNB to 5GC, a part of the data is split between gNB and NG eNB over the Xn interface.
SA mode of 5G will involve replacing the eNB with gNB and the EPC with a 5GC supporting service based interfaces. SA mode has two options defined as of now – option 2 and option 5. In SA option 2 the eNB is replaced by gNB and the EPC is replaced by 5GC and co-existence of 4G and 5G is possible by inter RAT mobility. SA option 2 enables the operator to fully utilize the ability of 5G and support eMBB, uRLLC and mMTC use cases. Interworking between 5GS and EPS for service continuity will be required.The next option of upgrading SA is option 5 in which LTE eNB will be upgraded to communicate to 5GC.
The Network Migration can follow the following path – From NSA Option 3 to NSA Option 4 to SA Option 2 Or NSA Option 3 to NSA Option 7 to SA Option 2
Vo5G summarizes all 5G voice/video communication solutions. Vo5G should include VoNR, VoeLTE, EPS FB (Evolved Packet System Fall Back), and RAT FB (RAT Fall Back). Irrespective of the network migration mode ESTSI has standardized the voice/video communication through 5G. After 5GC is introduced the voice service can be provided through IMS over 5GS and does not provide CSFB (Circuit Switch Fall Back) support and SRVCC (Single Radio Voice Call Continuity – required for voice service continuity between LTE and CS access) support in-order to simplify the network implementation. In the 5G NSA stage, voice service would be VoLTE, in 5G SA initial stage voice service would be provided using EPS Fall Back. In the mature stage of SA voice over NR needs to be supported with the option of RAT FB when the user moves out of 5G coverage.

















